Understanding Athletic Nutritional Needs
Athletes require a diet that optimizes energy, maintains endurance, and aids recovery. These nutritional needs differ from those of non-athletes due to the physical demands placed on the body. Based on extensive research and expert guidance from the American College of Sports Medicine, key nutrients have been identified for athletes.
- Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for high-intensity activities. They’re stored as glycogen in muscles and liver, providing fuel during workouts. Consuming 6-10 grams per kilogram of body weight daily ensures adequate stores.
- Proteins play a crucial role in muscle repair and growth. Their intake becomes critical after intense workouts. I include 1.2-2.0 grams per kilogram of body weight for sufficient protein, as recommended by sports nutritionists.
- Fats serve as a long-lasting energy source. They’re essential for long-duration, lower-intensity exercises. Healthy options like avocados, nuts, and olive oil supply necessary fatty acids without increasing health risks.
- Hydration, including water and electrolytes, supports optimal performance by preventing dehydration-related fatigue. While I aim to drink regularly throughout the day, it’s particularly important before, during, and after physical activities.
- Vitamins and minerals support various body functions. Athletes need these micronutrients for energy production, immunity, and bone health. Foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provide an array of these essential nutrients.
By understanding these nutritional needs, athletes can tailor their meal plans for peak performance. Each athlete’s requirements vary based on age, sex, sport, and training intensity.
Key Components of a Balanced Meal Plan

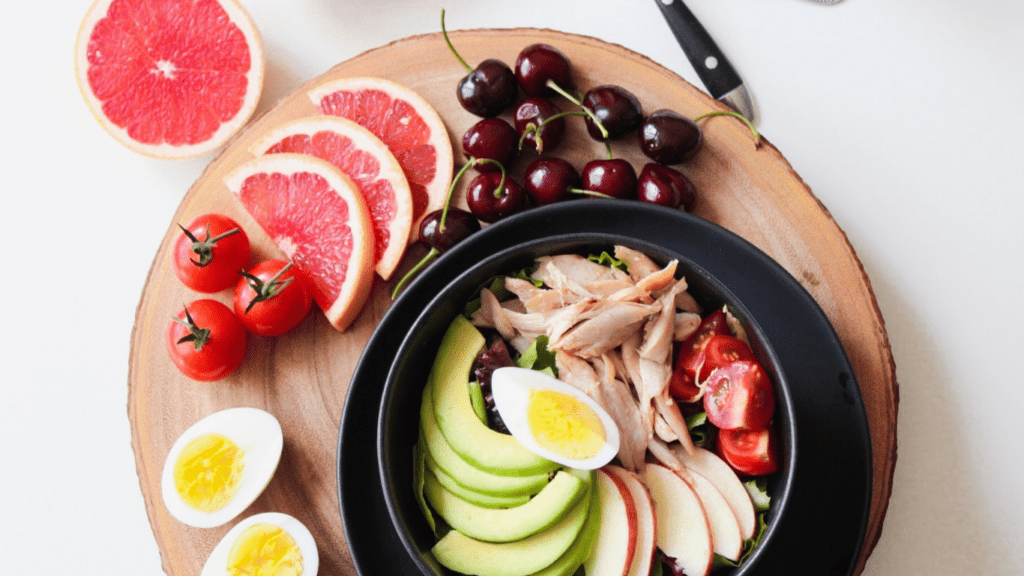
A balanced meal plan fuels peak athletic performance by incorporating essential nutrients. It focuses on macronutrients, micronutrients, and hydration.
Macronutrients
Macronutrients form the foundation of any effective meal plan. Carbohydrates supply quick and efficient energy, crucial for intense training sessions. I focus on:
- whole grains
- fruits
- vegetables
to ensure sustained energy release. Proteins aid in muscle repair; I include lean meats, dairy, and legumes for optimal muscle recovery. Fats, though often overlooked, provide long-lasting energy. I choose healthy fats like avocados, nuts, and olive oil for maintaining endurance.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients are vital for supporting various bodily processes. Vitamins like B-complex and C contribute to energy metabolism and immune function. Minerals such as calcium and iron promote bone health and oxygen transport. I ensure a diverse diet rich in colorful fruits and leafy greens to cover these needs.
Hydration
Hydration directly impacts athletic output. Adequate fluid intake prevents fatigue and maintains focus during performance. I keep water readily available and monitor electrolyte balance, especially after intense workouts, to sustain physical and mental power.
Meal Timing and Frequency
Athletes benefit from strategic meal timing, boosting energy and recovery. I’ll explore critical aspects of pre- and post-workout nutrition.
Pre-Workout Nutrition
Consuming energy-rich foods about 1-3 hours before exercise maximizes performance. I focus on carbohydrates like oatmeal or whole-grain bread, providing readily available energy. Including moderate protein from sources like yogurt helps sustain energy levels. I avoid high-fat or high-fiber foods before workouts, which may cause digestive discomfort.
Post-Workout Recovery
Post-exercise meals promote recovery and muscle repair. Within 30 minutes after training, consuming a combination of protein and carbohydrates is crucial. I often choose a shake with whey protein and a banana, ensuring muscle recovery and glycogen replenishment. Including electrolytes, perhaps through a sports drink, aids hydration and balances nutrients lost through sweat.
Tailoring Meal Plans for Different Sports
Understanding the specific nutritional needs of various sports can optimize an athlete’s performance. I’ll explore how meal plans differ for endurance sports and strength and power sports.
Endurance Sports
Endurance sports like marathons and triathlons require sustained energy output. Carbohydrates dominate the dietary intake, comprising 55-65% of total calories, to maintain glycogen stores. Complex carbs like whole grains and legumes provide steady energy. Pre-competition, I focus on carb-loading 2-3 days prior to maximize reserves.
Protein, accounting for 10-15% of calories, aids in muscle repair; sources include lean meats and dairy. Fats, though limited to 20-25%, come from nuts and oils for a slow energy release. Hydration with electrolytes, especially sodium and potassium, is crucial.
Strength and Power Sports
Sports emphasizing strength and power, such as weightlifting and sprinting, need a different nutrient focus. Protein intake rises to support muscle synthesis, forming 25-30% of daily calories.
Lean proteins, including chicken and fish, are ideal. Carbohydrates still play a role, making up 45-55% to fuel short bursts of energy. Fats, involved in hormone production, consist of 20-30% of the diet, with sources like avocados enhancing recovery. Timing is critical; I consume protein-rich meals post-workout for optimal muscle repair.
Practical Meal Planning Tips
Athletes can achieve peak performance by incorporating strategic meal planning practices. These practical approaches ensure they meet their nutritional needs and manage time effectively.
Batch Cooking and Prepping
Preparing meals in advance saves time and ensures that I always have nutritious food available. Cooking large quantities of staple ingredients, like grilled chicken, roasted vegetables, and quinoa, provides flexibility to create varied meals throughout the week.
Incorporating versatile proteins, carbohydrates, and healthy fats, such as olive oil and nuts, into meal prep boosts energy and satisfies hunger. For me, clear labeling and organized storage in airtight containers aid in quickly assembling meals before training sessions.
Snack and Supplement Choices
Between meals, strategic snacks sustain my energy levels and aid recovery. Opting for nutrient-dense options, such as Greek yogurt with berries or a banana with almond butter, offers a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats.
For supplement support, I rely on protein shakes post-workout for muscle recovery and electrolyte tablets during intense training to maintain hydration. Ensuring snacks and supplements are accessible helps me stay on track with my performance goals.







































































































































































































































































































































































































 Brodie Cani’s contributions to Make Athlete Action have been instrumental in delivering cutting-edge sports science news to the platform’s audience. With a background in sports research, Brodie is dedicated to translating the latest scientific advancements into actionable insights for athletes. His work ensures that readers stay informed about the newest trends and discoveries that can impact their training and performance. Brodie’s dedication to accuracy and relevance has helped shape Make Athlete Action into a reliable resource for anyone looking to stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of sports science.
Brodie Cani’s contributions to Make Athlete Action have been instrumental in delivering cutting-edge sports science news to the platform’s audience. With a background in sports research, Brodie is dedicated to translating the latest scientific advancements into actionable insights for athletes. His work ensures that readers stay informed about the newest trends and discoveries that can impact their training and performance. Brodie’s dedication to accuracy and relevance has helped shape Make Athlete Action into a reliable resource for anyone looking to stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of sports science.